Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ono, Ayako; Suzuki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/07
The mechanism of critical heat flux (CHF) for higher system pressure remains to be clarified, even though it is important to evaluate the CHF for the light water reactor (LWR) which is operated under the high pressure condition. In this study, the process of bubble coalescence was simulated by using a computational multi-fluid dynamics (CMFD) simulation code TPFIT under various system pressure in order to investigate the behavior of bubbles as a basic study. The growth of bubbles was simulated by blowing of vapor from a tiny orifice simulating bubble bottom. One or four orifices were located on the bottom surface in this simulation study. The numerical simulations were conducted by varying the pressure and temperature.
Tsuru, Daigo; Sakurai, Shinji; Nakamura, Shigetoshi; Ozaki, Hidetsugu; Seki, Yohji; Yokoyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Satoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.1403 - 1406, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ezato, Koichiro; Suzuki, Satoshi; Seki, Yohji; Mori, Kensuke; Yokoyama, Kenji; Escourbiac, F.*; Hirai, Takeshi*; Kuznetsov, V.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.1281 - 1284, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:95.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is now devoting to development of Full-W ITER divertor outer vertical target (OVT), especially, PFU that needs to withstand the repetitive heat load as high as 20MW/m . JAEA have succeeded in demonstrating that the soundness of a bonding technology is sufficient for the full-W ITER divertor. For the development of bonding technology, the load carrying capability test on the W monoblock with a leg attachment to an OVT support structure was carried out and shows that the attachment can withstand against the uniaxial load more than 20 kN which is three times higher than the IO requirement. JAEA manufactured 6 small-scale mock-ups and tested under the repetitive heat load of 10 and 20 MW/m
. JAEA have succeeded in demonstrating that the soundness of a bonding technology is sufficient for the full-W ITER divertor. For the development of bonding technology, the load carrying capability test on the W monoblock with a leg attachment to an OVT support structure was carried out and shows that the attachment can withstand against the uniaxial load more than 20 kN which is three times higher than the IO requirement. JAEA manufactured 6 small-scale mock-ups and tested under the repetitive heat load of 10 and 20 MW/m to examine the durability of the divertor structure including W tile bonding and the cooling tube. All of the mock-ups could survived 5000 cycles at 10 MW/m
to examine the durability of the divertor structure including W tile bonding and the cooling tube. All of the mock-ups could survived 5000 cycles at 10 MW/m and 1000 cycles 20 MW/m
and 1000 cycles 20 MW/m with no failure such as debonding of the W tile and water leak from the cooling tube. The number of cycles at 20 MW/m
with no failure such as debonding of the W tile and water leak from the cooling tube. The number of cycles at 20 MW/m is three times longer than the requirement of ITER divertor.
is three times longer than the requirement of ITER divertor.
Yoshida, Hajime; Yokoyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Akiba, Masato
Review of Scientific Instruments, 77(4), p.043502_1 - 043502_4, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)New beam extraction electrode has been developed for a 100 eV level, high-flux, large irradiation area, and steady-state ion beam source to study about plasma wall interaction in fusion reactors. This electrode has two specific features; one is the structure has sub-millimeter order of spherical multi-aperture triode electrodes and the other is to utilize the plasma sheath for ion acceleration. Obtained ion fluxes ware from 1.5 1020 H/m
1020 H/m s to 5.3
s to 5.3 1020 H/m
1020 H/m s with the energy from 28 eV/H to 102 eV/H. These values are comparable to those of conventional high flux ion source in spite of such an extremely low energy.
s with the energy from 28 eV/H to 102 eV/H. These values are comparable to those of conventional high flux ion source in spite of such an extremely low energy.
Yoshida, Hajime; Yokoyama, Kenji; Taniguchi, Masaki; Ezato, Koichiro; Suzuki, Satoshi; Akiba, Masato
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.361 - 366, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)A 100 V level, high-flux, large area and steady-state ion beam acceleration has been developed for the investigation of the interactions between fusion edge plasmas and plasma facing materials. We have developed the new electrodes and installed them in the Super Low Energy Ion Source (SLEIS). Obtained hydrogen ion flux is comparable to those of conventional high-flux ion source ( 1020 H/m
1020 H/m s), though the accelerated voltage is extremely low (60-200 eV). This 100 V level ion beam acceleration will be useful to investigate the plasma wall interaction in divertor.
s), though the accelerated voltage is extremely low (60-200 eV). This 100 V level ion beam acceleration will be useful to investigate the plasma wall interaction in divertor.
Ezato, Koichiro; Suzuki, Satoshi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Akiba, Masato
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.347 - 354, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:63.1(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ezato, Koichiro; Suzuki, Satoshi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Akiba, Masato
Fusion Engineering and Design, 75-79, p.313 - 318, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.74(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Bakhtiari, M.; Tamai, Hiroshi; Kawano, Yasunori; Kramer, G. J.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Nakano, Tomohide; Kamiya, Kensaku; Yoshino, Ryuji; Miura, Yukitoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(5), p.318 - 325, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:78.65(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In the previous works we had shown that injecting a mixture of large amounts of hydrogen and small amounts of argon can terminate a tokamak discharge quickly with avoiding runaway electron generation. In this work we have done the same experiments but with different gases in addition to argon. In fact we compared the effect of the puffing of argon, krypton, and xenon gases with and without simultaneous hydrogen gas puffing on disruption mitigation. We observed that injecting all impurities in the form of an admixture in hydrogen lead to faster plasma shutdowns with less runaway electron generation. We also found that injecting krypton gas (with or without hydrogen) seems to be a good candidate for plasma shutdown purposes since it induces low heat flux to divertor plates and avoids runaway electron generation more effectively.
Hirai, Takeshi*; Ezato, Koichiro; Majerus, P.*
Materials Transactions, 46(3), p.412 - 424, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:111 Percentile:90.2(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ezato, Koichiro; Dairaku, Masayuki; Taniguchi, Masaki; Sato, Kazuyoshi; Suzuki, Satoshi; Akiba, Masato; Ibbott, C.*; Tivey, R.*
Fusion Science and Technology, 46(4), p.530 - 540, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:66.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)The first fabrication and heating test of a large-scale CFC monoblock divertor mock-up using annular flow concept have been performed to demonstrate its manufacturability and thermo-mechanical performance. Prior to the fabrication of the mock-up, brazed joint tests between the CFC monoblock and the CuCrZr tube have been carried out to find the suitable heat treatment mitigating loss of the high mechanical strength of the CuCrZr material. Basic mechanical examination on CuCrZr undergoing the brazing heat treatment and FEM analyses are also performed to support the design of the mock-up. High heat flux tests on the large-scale divertor mock-up have been performed in an ion beam facility. The mock-up has successfully withstood more than 1,000 thermal cycles of 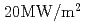 for 15 s and 3,000 cycles more than
for 15 s and 3,000 cycles more than 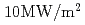 for 15 s, which simulates the heat load condition of the ITER divertor. No degradation of the thermal performance of the mock-up has been observed throughout the thermal cycle test.
for 15 s, which simulates the heat load condition of the ITER divertor. No degradation of the thermal performance of the mock-up has been observed throughout the thermal cycle test.
Ezato, Koichiro
Koon Gakkai-Shi, 30(5), p.248 - 255, 2004/09
no abstracts in English
Ezato, Koichiro; Suzuki, Satoshi; Sato, Kazuyoshi; Akiba, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(1), p.820 - 824, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper presents thermal fatigue experiments of a cooling tube with a helical triangular fin on its inner cooled surface, namely a 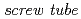 . The screw thread is directly shaped in a CuCrZr heat sink bar as a cooling channel. Slits with the width of 1.5 mm are machined at the heated side of the heat sink. The thermal fatigue experiments are carried out at 20 and 30
. The screw thread is directly shaped in a CuCrZr heat sink bar as a cooling channel. Slits with the width of 1.5 mm are machined at the heated side of the heat sink. The thermal fatigue experiments are carried out at 20 and 30 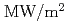 by using an electron beam irradiation facility in JAERI. Water leakages from fatigue cracks, which locate at the slit of the heat sink, occurred at around 4500th and 1400th cycles at 20 and 30
by using an electron beam irradiation facility in JAERI. Water leakages from fatigue cracks, which locate at the slit of the heat sink, occurred at around 4500th and 1400th cycles at 20 and 30 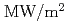 , respectively. These results show good agreement with lifetime predictions using Manson-Coffin's law based on finite element analyses. Fractographic observations reveal that the fatigue cracks start from the outer heated surface at the slit region of the cooling channel and propagate toward its inner surface.
, respectively. These results show good agreement with lifetime predictions using Manson-Coffin's law based on finite element analyses. Fractographic observations reveal that the fatigue cracks start from the outer heated surface at the slit region of the cooling channel and propagate toward its inner surface.
Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Sakasegawa, Hideo*; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Zinkle, S. J.*; Klueh, R. L.*; Koyama, Akira*
Fusion Materials Semiannual Progress Report for the Period Ending (DOE/ER-0313/35), p.33 - 36, 2004/04
Extraction replica samples were prepared from F82H-IEA, F82H HT2, JLF-1 and ORNL9Cr to analyze the precipitate distribution. The samples were examined to obtain precipitate size distribution with TEM and to analyze chemical composition distribution with SEM. Back-scattered electron imaging was found to be the effective way to separate Ta-rich precipitate from other precipitates. Results showed that most of the precipitates were M23C6, and the shape is a round ellipsoid in F82H-IEA and HT2, but was a long ellipsoid in JFL-1 and ORNL9Cr. It was also found that MX precipitates were few and large and contain Ti in F82H-IEA and HT2, but a lot of fine MX precipitates without Ti were observed in JLF-1 and ORNL9Cr.
Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Sakasegawa, Hideo*; Zinkle, S. J.*; Klueh, R. L.*; Koyama, Akira*
Fusion Materials Semiannual Progress Report for the Period Ending (DOE/ER-0313/35), p.30 - 32, 2004/04
Extraction residue was made from several HFIR 11J-irradiated RAFs, and the mass change was measured to investigate the irradiation-enhanced change in precipitation. Two different types of filter with coarse and fine pores were used in order to separate the difference of irradiation effects between larger and smaller precipitates. Unirradiated specimens were examined as well. Results suggest that during irradiation the mass of larger precipitates increased in F82H-IEA, Ni-doped F82H, JLF-1 and ORNL9Cr, fine precipitates disappeared in JLF-1, and fine precipitates increased in Ni-doped F82H.
Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Sakasegawa, Hideo*; Payzant, E. A.*; Zinkle, S. J.*; Klueh, R. L.*; Koyama, Akira*
Fusion Materials Semiannual Progress Report for the Period Ending (DOE/ER-0313/35), p.37 - 40, 2004/04
XRD analyses were performed on the extraction residue of HFIR 11J-irradiated RAFs to investigate the overall precipitate character. Un-irradiated and aged specimens were examined as well. Results suggested that the distinctive peaks of M23C6 (M; Cr, Fe, W) were observed on all specimens. Peaks possibly related to MX (M;Ta,Ti,V : X ; C, N) were observed on the specimens extracted from un-irradiated JLF-1 and ORNL9Cr, but those peaks were not observed on irradiated specimens.
Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Sokolov, M. A.*; Klueh, R. L.*; Ando, Masami
Fusion Materials Semiannual Progress Report for the Period Ending (DOE/ER-0313/35), p.58 - 60, 2004/04
1TCT fracture toughness specimens of F82H-IEA steel were fatigue precracked and sliced in specimen thickness wise for microstructure analysis around the precrack. The microstructure around the precrack was observed by optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), orientation imaging microscopy (OIM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). TEM samples around the crack front were prepared by focused ion beam (FIB) processor. The fracture surfaces of tested 1TCT specimens were also observed. OM observation showed that the precrack penetration was straight in the beginning, and then tended to follow a prior austenite grain boundary and to branch into 2 to 3 directions at the terminal. SEM and OIM observations revealed that the both microstructures around the precracks and ahead of the precrack had turned into cell structure, which is the typical microstructure of fatigue-loaded F82H. TEM images and inverse pole figures obtained from the crack-front region confirmed this structure change.
Toda, Saburo*; Yuki, Kazuhisa*; Akimoto, Hajime
JAERI-Tech 2004-008, 58 Pages, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
 ions
ionsLee, C. G.; Omura, Takahito*; Takeda, Yoshihiko*; Matsuoka, Saburo*; Kishimoto, Naoki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 326(2-3), p.211 - 216, 2004/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Magnesium aluminate spinel of single crystal was irradiated with 60 keV Cu at a dose rate up to 100
at a dose rate up to 100  A/cm
A/cm , to a total dose of 3
, to a total dose of 3 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm , in order to study changes in hardness and step-height swelling by high-flux implantation. Hardness determined by nano-indentation measurements steeply decreased with implantation. There is a strong negative correlation between dose-rate dependences of the hardness and the step-height swelling: the former decreases as the latter increases. The Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry (RBS)/channeling measurements showed that the spinel is not completely amorphized over the dose-rate range in this study, and the radiation-induced softening observed is not due to amorphization. Results of optical absorbance suggested that radiation-induced point defects and their clusters on the anion sublattices of the spinel played an important role in the radiation-induced swelling under high-flux ion implantation.
, in order to study changes in hardness and step-height swelling by high-flux implantation. Hardness determined by nano-indentation measurements steeply decreased with implantation. There is a strong negative correlation between dose-rate dependences of the hardness and the step-height swelling: the former decreases as the latter increases. The Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry (RBS)/channeling measurements showed that the spinel is not completely amorphized over the dose-rate range in this study, and the radiation-induced softening observed is not due to amorphization. Results of optical absorbance suggested that radiation-induced point defects and their clusters on the anion sublattices of the spinel played an important role in the radiation-induced swelling under high-flux ion implantation.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Hasegawa, Akira*; Sato, Manabu*; Abe, Katsunori*; Hiraoka, Yutaka*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 324(1), p.62 - 70, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:90.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, stress-relieved specimens and recrystallized specimens of pure Mo and Mo-Re alloys (Re content=2,4,5,10,13 and 41wt%) were neutron irradiated up to 20dpa at various temperatures (681-1072K). On microstructure observation, sigma phase and chi phase precipitates were observed in all irradiated Mo-Re alloys. Voids were observed in all irradiated specimen, and dislocation loops and dislocations were observed in the specimens that were irradiated at lower temperatures. On Vickers hardness testing, all of the irradiated specimens showed hardening. Especially Mo-41Re were drastically embrittled after irradiation at 874K or less. From these results, authors discuss about relation between microstructure development and radiation hardening, embrittlement, and propose the most efficient Re content and thermal treatment for Mo-Re alloys to be used under irradiation condition.
Akiba, Masato; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Enoeda, Mikio; Nishitani, Takeo; Konishi, Satoshi
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 79(9), p.929 - 934, 2003/09
no abstracts in English